Modern Renewal
Electrification
The earth needs a sabbath in the modern age, especially the land and sea, where carbon is accumulating from fossil fuel burning. Electrification is the most direct way to cleanse the skies and seas of pollutants, with carbon driving climate change the one of greatest urgency. Because the electrical grid is quickly moving to greater proportions of renewable energy, primarily wind and solar, transitioning to technologies powered by electricity, rather than fossil fuels, offers a pathway to eliminating carbon emissions.
Heating
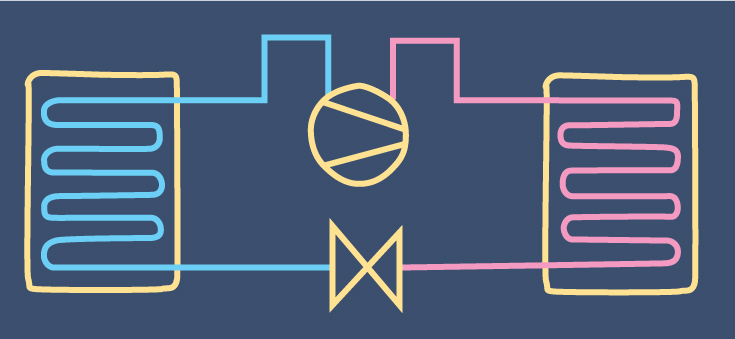
Emissions from heating can be dramatically reduced by moving from fossil fuels to electrically powered heat pumps. Heat pumps can be air source, where heat is drawn from the surrounding air, or ground source, where heat is drawn from the ground, geothermal.
Transportation
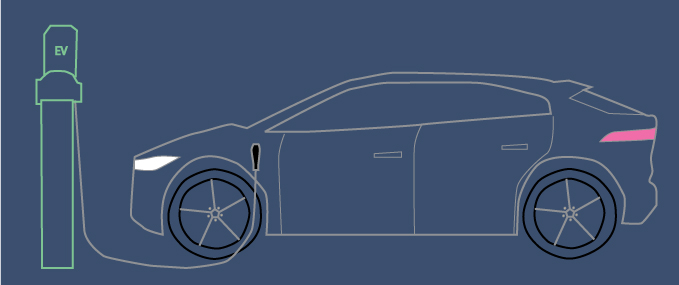
Electric vehicles, powered by batteries, offer far more efficient motors, even operating emission free if the grid is powered by renewables. They have numerous performance advantages over gas-powered vehicles, such as far fewer parts (less to break) and better torque, although challenges remain, such as charging speed and charger availability.
Appliances
Energy efficiency technologies offer significant potential for reducing climate pollution. Light emitting diodes (LEDs) lights are more efficient, cheaper, less toxic, and longer lasting than traditional forms of lighting. Smart, programmable thermostats and zoned heating and cooling offer considerable opportunity for improving building efficiency. Induction stoves provide efficient electric, and highly controllable heat for cooking.
Biophilic Design
Biophilic design is an approach to building connecting spaces to their natural surroundings. It is based on the idea that humans are inherently connected to nature and incorporating living spaces with nature is healthier and more sustainable. Economically, people spend considerable money to spend time in nature are willing to spend more money on spaces properly integrated with nature. Vegetation replacing small segments of concrete and lawn grass, nature wastelands, can have immense impact.
Natural Landscape
Grass lawns, standard land coverage for residences and businesses for much of the world, are effectively deserts. They are managed with large amounts of water, pesticides, and climate pollution with lawn equipment. Yet, they provide minimal water handling and animal habitat. Lawns can be replaced with natural landscapes, including native grasses, trees, good for pollinators and handling water. Replace mowing time with weeding. Do it right so it looks well kept.
Rain Gardens

Green infrastructure like rain gardens leverage plants and soil to retain water and filter pollutants. They improve flood control, ground water retention. and water quality. They are typically populated with native plants providing habitat, such as for pollinating insects.
Green Infrastructure

Green infrastructure includes plant and soil systems that filter and absorb rainwater where it falls. This contrasts gray infrastructure, the system of gutters, pipes, and tunnels that carries rainwater to waterways. The presence of such infrastructure can provide heat management, cleaner air and water, flood protection, habitat, and aesthetic value.
